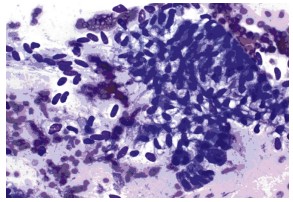
The Critical Role of Cytopathology in EUS-FNA
Introduction to Cytology in EUS-FNA
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration (EUS-FNA) is a pivotal diagnostic procedure in gastroenterology, offering a minimally invasive method to sample lesions within or adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract. The success of this technique not only relies on the skill of the endosonographer but also on the intricate analysis of the obtained samples by cytopathologists. Effective communication between these professionals is paramount for a successful EUS-FNA service.
Key to Success: Communication and Early Involvement
The Endosonographer-Cytopathologist Partnership
The collaboration between the endosonographer and the cytopathologist cannot be overstated. This partnership begins with clear communication regarding the clinical context and the specific areas of concern that the procedure aims to address. A well-informed cytopathologist can provide targeted feedback, improving the diagnostic yield of the EUS-FNA.
Establishing an EUS-FNA Service
For healthcare facilities looking to establish an EUS-FNA service, involving a cytopathology service from the onset is crucial. Early involvement ensures that the necessary infrastructure, including staffing and equipment, is tailored to meet the specific needs of this diagnostic procedure. This proactive approach facilitates a seamless workflow, from sample collection to analysis and diagnosis.
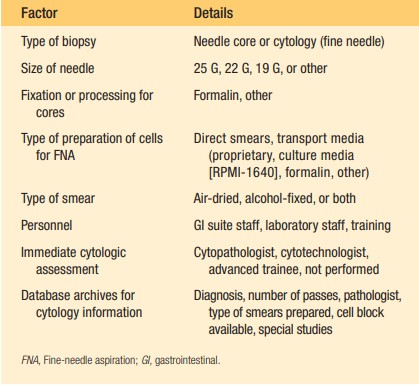
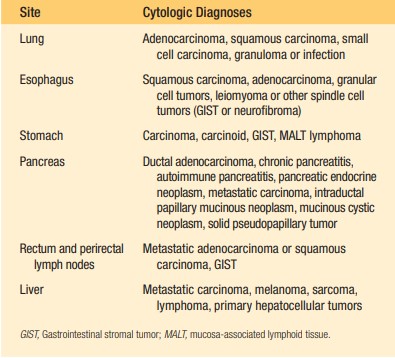
Algorithmic Approach in Diagnostics
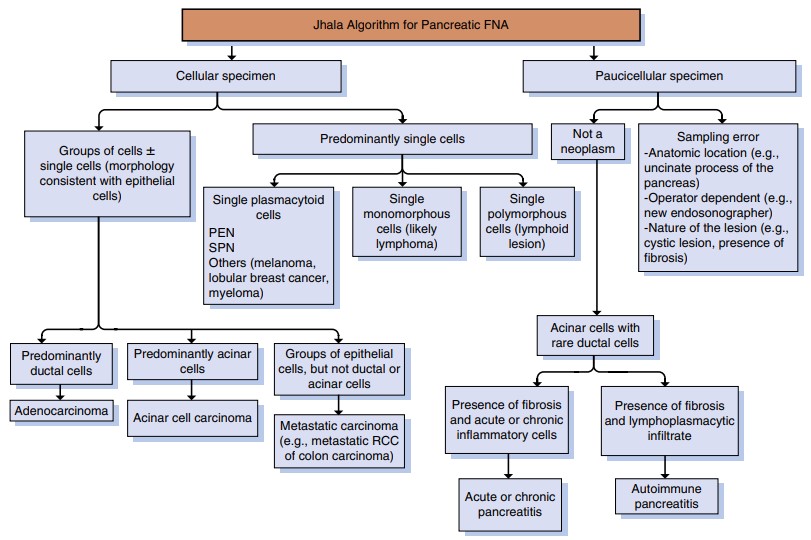
Implementing an algorithmic approach to diagnosing patients through EUS-FNA is instrumental in achieving accurate outcomes. This structured methodology guides the endosonographer and cytopathologist through a series of steps, from the initial assessment to the final diagnosis. Such an approach ensures that all potential diagnoses are considered and that the most appropriate tests are conducted, thereby minimizing the risk of oversight or error.
Facilitating Correct Diagnosis
An algorithmic diagnostic approach benefits patients by streamlining the process to arrive at the correct diagnosis efficiently. It allows for the consideration of all relevant factors, including the patient’s history, imaging findings, and the cytological characteristics of the sample. By systematically evaluating these elements, clinicians can make informed decisions, enhancing the accuracy of the diagnosis and the subsequent treatment plan.
Conclusion
The role of cytopathology in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration is fundamental to the success of this diagnostic procedure. Effective communication between endosonographers and cytopathologists, early involvement of cytopathology services, and an algorithmic approach to diagnosis are key elements that enhance the accuracy and efficiency of EUS-FNA. As these practices become more integrated into the workflow, patients stand to benefit from more precise diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for personal medical advice.
Learn More About Our Gastroenterology Services
Contact Us for More Information
