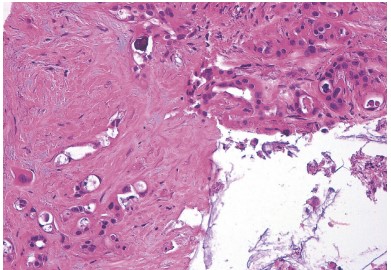
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy (EUS-FNB)
Introduction to Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy (EUS-FNB) represents a significant advancement in the diagnostic capabilities within the field of gastroenterology. Offering a minimally invasive route to obtain tissue samples from lesions within or adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract, EUS-FNB is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. However, the technique’s success heavily depends on the choice of needle and the expertise of the endosonographer.
Challenges and Solutions in EUS-FNB
Overcoming Limitations of EUS-FNA
While Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration (EUS-FNA) is highly accurate, it falls short in fully characterizing certain neoplasms due to limitations in obtaining histological samples. Additionally, the lack of cytology expertise can diminish the perceived utility of EUS. The advent of fine-needle biopsy (FNB) techniques and needles aims to address these challenges by providing high-quality histologic samples, thus enhancing diagnostic accuracy and utility.
The Role of Needle Gauge and Design
- Standard Needles: Traditional 19-G and 22-G fine-needle aspiration needles, with or without the application of high negative pressure, have been reliable in obtaining quality histologic samples across various indications. These needles serve as the cornerstone in EUS-FNB, balancing the need for tissue quality with procedural ease.

- ProCore Needles: The novel 19-G and 22-G ProCore needles have shown a high yield in obtaining histologic samples, making them favorable choices for comprehensive tissue analysis. However, the 25-G ProCore needle appears less suitable for histological purposes due to its reduced ability to acquire adequate tissue.

- Emerging Needle Technologies: Although data is limited, newer needles like the 20-G ProCore, SharkCore, and Acquire needles show promising results. These advancements in needle design are anticipated to further improve the yield and quality of histologic samples, enhancing the diagnostic precision of EUS-FNB.

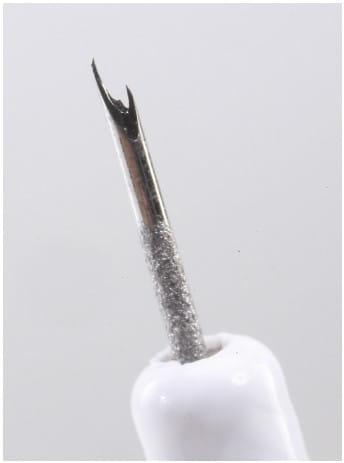

Future Perspectives in EUS-FNB
The evolution of needle technology and biopsy techniques is expected to refine differential diagnostic capabilities significantly. This progress will not only encourage wider utilization of endoscopic ultrasound but also pave the path towards targeted therapies and better monitoring of treatment responses. As these technologies continue to develop, the gastroenterology field stands on the cusp of a new era in diagnostic and therapeutic precision.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy is evolving as a cornerstone technique in the diagnosis and management of gastrointestinal diseases. By leveraging advanced needle technologies and refined biopsy techniques, gastroenterologists can achieve unparalleled diagnostic accuracy, ultimately improving patient care. As we move forward, the integration of these innovations will undoubtedly expand the boundaries of what’s possible in gastroenterology diagnostics.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for personal medical advice.
Learn More About Our Gastroenterology Services
Contact Us for More Information
