Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Rectal Cancer: Enhancing Therapeutic Decision-Making
The Significance of Nodal Status in Rectal Cancer
The accurate assessment of nodal status in rectal cancer is paramount in guiding therapeutic decisions. As the understanding of rectal cancer’s complexity grows, the role of nodal involvement in determining treatment pathways becomes increasingly critical. This importance underscores the need for precise diagnostic methods to evaluate the locoregional spread of the disease.
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) in Clinical Staging
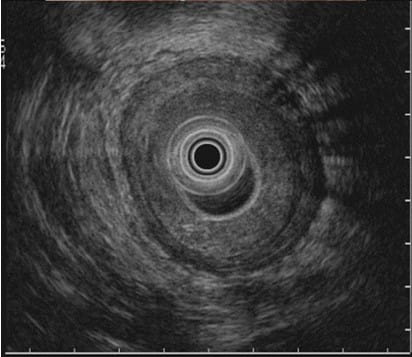
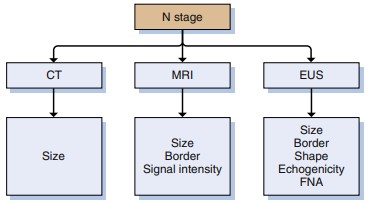
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS), combined with fine-needle aspiration (FNA), has emerged as an indispensable tool in the locoregional clinical staging of rectal cancer. This technique allows for the detailed visualization of the rectal wall layers and the perirectal space, enabling the identification of nodal disease with remarkable accuracy.
The Impact of EUS FNA on Staging and Management
EUS FNA’s capability to predict iliac vessel node disease represents a significant advancement in rectal cancer management. By accurately upstaging 7% of patients who initially present for evaluation, EUS FNA ensures that therapeutic decisions are based on a comprehensive understanding of the disease’s extent. This precision is crucial for tailoring treatment strategies that are aligned with the patient’s specific condition.
Limitations and Considerations
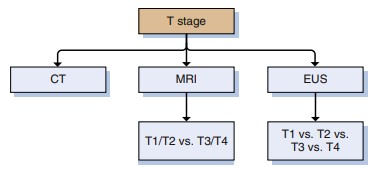
Despite its advantages, EUS has limitations, particularly in T-staging accuracy. However, its utility in identifying perirectal space nodal disease remains unparalleled. Clinicians should approach EUS staging with caution following neoadjuvant therapy, as treatment effects can alter the interpretability of findings.
The Role of EUS FNA in Postoperative Surveillance
EUS FNA’s value extends into the postoperative period, where it serves as a key component of surveillance. Its ability to biopsy the extramural perirectal space is especially beneficial for establishing the presence of local disease recurrence. This capability ensures timely and appropriate interventions, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Ultrasonography, particularly when combined with fine-needle aspiration, plays a crucial role in the staging and management of rectal cancer. Its precision in assessing nodal status and local disease extent is indispensable for guiding therapeutic decisions. Despite some limitations, the benefits of EUS FNA, especially in postoperative surveillance, highlight its importance in the comprehensive care of rectal cancer patients.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for personal medical advice.
Learn More About Our Gastroenterology Services
Contact Us for More Information
