Endoscopic Ultrasonography in Evaluating Posterior Mediastinal Lesions
Explore the critical role of Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) in diagnosing and differentiating posterior mediastinal lesions, enhancing the accuracy of clinical decisions.
Understanding Posterior Mediastinal Lesions with Endoscopic Ultrasonography
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) has emerged as a pivotal tool in the evaluation and management of posterior mediastinal lesions. It serves as an essential technique for distinguishing between benign and malignant conditions in this area.
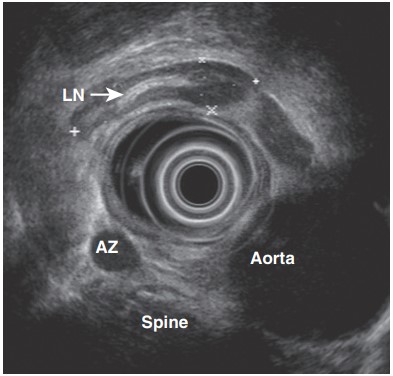
Differentiating Benign and Malignant Mediastinal Lymph Nodes
Traditional criteria for differentiating benign from malignant mediastinal lymph nodes have limitations in accuracy. EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS FNA) fills this gap, providing a more reliable method for making sound clinical decisions.
High Accuracy in Diagnosing Posterior Mediastinal Malignancies
The overall accuracy of transesophageal EUS FNA for diagnosing posterior mediastinal malignancies exceeds 90%. This high level of precision significantly aids in the early detection and treatment planning for these conditions.
Effective in Diagnosing Lymphoma
The diagnosis of lymphoma in the posterior mediastinum primarily relies on cytology and flow cytometry studies on EUS FNA and core biopsy specimens. This approach ensures a comprehensive and accurate diagnosis, crucial for effective treatment.
Assessing Granulomatous Diseases
EUS FNA proves valuable in diagnosing granulomatous diseases involving the mediastinum, such as sarcoidosis, histoplasmosis, and tuberculosis. This technique allows for precise identification and assessment of these conditions.
Handling Mediastinal Cysts with Caution
While most mediastinal cysts are benign, EUS FNA is generally avoided due to the high risk of infection. In cases where malignancy is highly suspected, a single puncture and full drainage are recommended, along with the administration of antibiotics.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Ultrasonography has become an indispensable tool in the evaluation of posterior mediastinal lesions. Its ability to distinguish between benign and malignant conditions with high accuracy greatly assists clinicians in formulating effective treatment strategies for their patients.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for personal medical advice.
Learn More About Our Gastroenterology Services
Contact Us for More Information
