Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections
Dr. Ali recognized as one of the best gastroenterologist in Karachi, offers Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-guided drainage for patients with pancreatic fluid collections, providing a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods.
Introduction to Pancreatic Fluid Collections Management
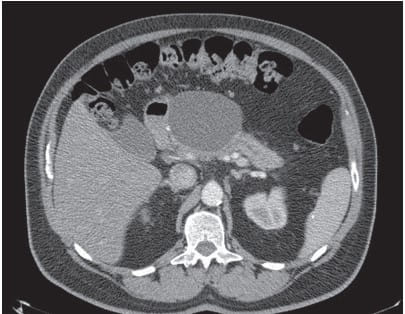
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are a common complication of acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, or abdominal trauma. Accurate recognition of the type of PFC is paramount for appropriate management. The introduction of Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)-guided drainage has revolutionized the treatment of these conditions, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery with comparable outcomes.
The Importance of Recognizing Different Types of Pancreatic Fluid Collections
Identifying Pseudocysts and Walled-Off Necrosis
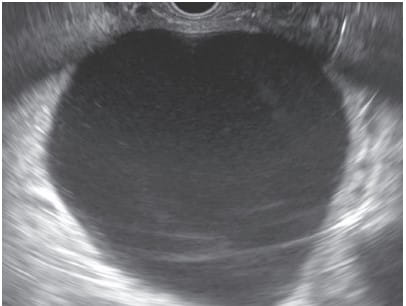
The differentiation between pancreatic pseudocysts and walled-off necrosis (WON) is crucial, as it dictates the management strategy. Pseudocysts, which are encapsulated collections of pancreatic fluid devoid of necrosis, often result from acute pancreatitis or trauma. In contrast, WON is characterized by a mature, encapsulated collection of pancreatic and/or peripancreatic necrosis that has evolved from acute necrotizing pancreatitis.
EUS-Guided Drainage: The Preferred Treatment for Pseudocysts
EUS-guided drainage has become the treatment of choice for managing pancreatic pseudocysts, demonstrating clinical outcomes that are comparable to those of surgical cystogastrostomy. This minimally invasive technique utilizes endoscopic ultrasonography to accurately locate the pseudocyst and create a direct connection between the cyst and the gastrointestinal tract, allowing for efficient drainage.
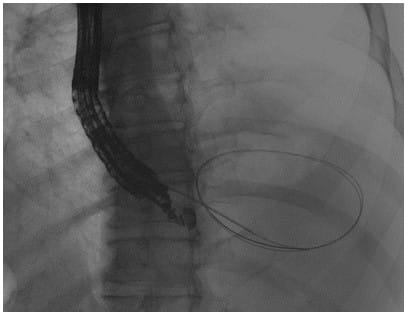
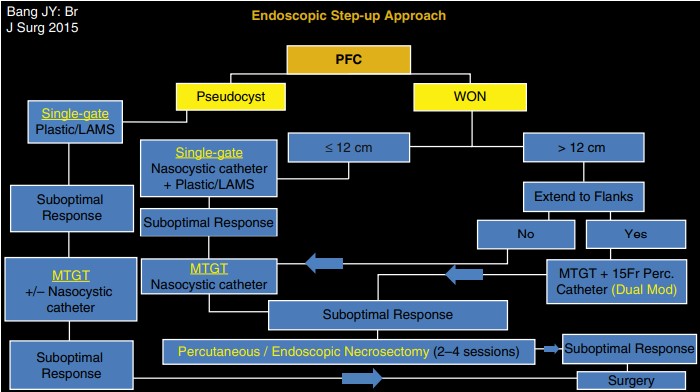
Managing Walled-Off Necrosis: A Tailored Approach
The endoscopic management of WON is more complex due to the presence of necrotic tissue within the fluid collection. Treatment is tailored to the size and location of the fluid collection and may require a more aggressive approach. An algorithmic step-up approach is often employed, involving the creation of multiple transmural tracts, percutaneous drain insertion, and, if necessary, endoscopic necrosectomy to remove necrotic debris.
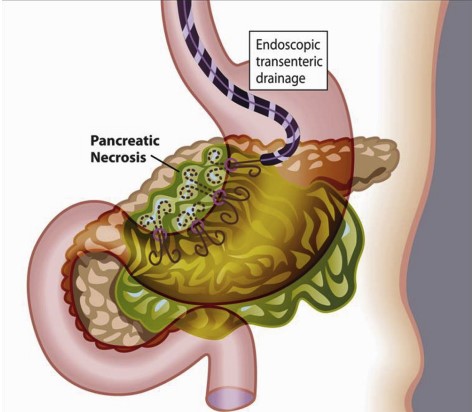
The Role of DPDS Identification in WON Management
Disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome (DPDS) is a condition often associated with WON, characterized by a discontinuity of the pancreatic duct. Identifying DPDS is essential, as affected patients require the placement of plastic transmural stents indefinitely to minimize the risk of recurrence. This highlights the need for a comprehensive evaluation and customized treatment planning in patients with WON.
Conclusion
The advent of EUS-guided drainage techniques has significantly improved the management of pancreatic fluid collections, offering a less invasive yet effective alternative to traditional surgical methods. Recognizing the type of PFC, employing tailored management strategies for WON, and identifying conditions like DPDS are critical steps in ensuring successful outcomes. As technology and techniques continue to evolve, patients benefit from more precise and less invasive treatment options.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for personal medical advice.
Learn More About Our Gastroenterology Services
Contact Us for More Information
